An Open Synthetic Biology Toolkit for Engineering Reliable Genetic Circuits in Microbes in Soil: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{righttoc}} | {{righttoc}} | ||
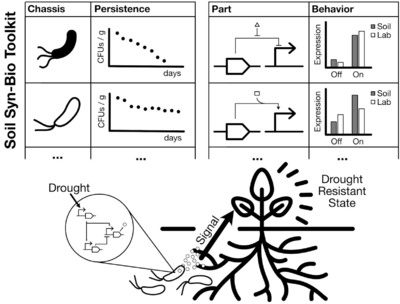
This goal of this project is to demonstrate the feasibility of an “open source” toolkit for soil synthetic biology, with the goal of bootstrapping a larger effort that would enable the use of engineered microbes to understand and modulate the complex dynamics of the rhizosphere. We will identify and characterize genetically tractable microbes capable of long-term persistence; create a toolbox of genetic parts for gene circuits and pathways in soil conditions; and design, build, and test a stimulus-response circuit operating in soil. Long-term applications include engineering microbial communities to optimize nutrient uptake and improve survival against environmental hazards such as drought, toxins, or pathogens. | This goal of this project is to demonstrate the feasibility of an “open source” toolkit for soil synthetic biology, with the goal of bootstrapping a larger effort that would enable the use of engineered microbes to understand and modulate the complex dynamics of the rhizosphere. We will identify and characterize genetically tractable microbes capable of long-term persistence; create a toolbox of genetic parts for gene circuits and pathways in soil conditions; and design, build, and test a stimulus-response circuit operating in soil. Long-term applications include engineering microbial communities to optimize nutrient uptake and improve survival against environmental hazards such as drought, toxins, or pathogens. | ||
{| cellpadding=0 cellspacing=0 width=80% | {| cellpadding=0 cellspacing=0 width=80% | ||
| Line 23: | Line 18: | ||
=== Objectives === | === Objectives === | ||
[[Image:RSI-soil_syn_bio.png|right|400px]] | [[Image:RSI-soil_syn_bio.png|right|400px]] | ||
* Identify & characterize genetically-tractable microbes capable of long-term soil persistence | |||
* Create a toolbox of genetic parts for building gene circuits for long-term soil deployment | |||
* Design, build, and test a stimulus-response circuit with predictable function in soil | |||
=== References === | === References === | ||
Revision as of 05:08, 20 July 2020
This goal of this project is to demonstrate the feasibility of an “open source” toolkit for soil synthetic biology, with the goal of bootstrapping a larger effort that would enable the use of engineered microbes to understand and modulate the complex dynamics of the rhizosphere. We will identify and characterize genetically tractable microbes capable of long-term persistence; create a toolbox of genetic parts for gene circuits and pathways in soil conditions; and design, build, and test a stimulus-response circuit operating in soil. Long-term applications include engineering microbial communities to optimize nutrient uptake and improve survival against environmental hazards such as drought, toxins, or pathogens.
|
Current participants: Additional participants: |
Collaborators: Past participants:
|
Objectives
- Identify & characterize genetically-tractable microbes capable of long-term soil persistence
- Create a toolbox of genetic parts for building gene circuits for long-term soil deployment
- Design, build, and test a stimulus-response circuit with predictable function in soil
References
- Metabolic engineering of Pseudomonas putida for production of vanillylamine from lignin-derived substrates. João Heitor Colombelli Manfrão-Netto, Fredrik Lund, Nina Muratovska, Elin M. Larsson, Nádia Skorupa Parachin, Magnus Carlquist. Microbial Biotechnology, 14( 6), 2448– 2462, 2021.
This work was supported by the Resnick Sustainability Institute.
|
|
|