Control Design for Cyberphysical Systems Using Slow Computing
From Murray Wiki
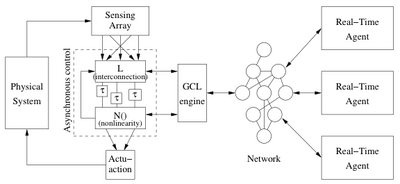
This project seeks to develop new, systematic methods for the design of control systems that can work in the presence of slow computing elements. The development of such an architecture has the possibility of providing new ways of integrating control into systems where large amounts of fast computation are not easily available, either due to limitations on power, physical size or choice of computing substrate. This project is supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF), award number 0931746.
Current participants:
|
Past participants |
Objectives
- Develop an architecture for control using slow computing
- Develop new theory and and tools for design of controller for cyberphysical systems that scale to slow computing
- Demonstrations of the our methodology on university scale experiments in micro-vehicles.
Publications
- A bio-plausible design for visual pose stabilization, Shuo Han, Andrea Censi, Andrew D Straw, Richard M Murray. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2010.
- Simple Delay-Based Implementation of Continuous-Time Controllers, Javad Lavaei, Somayeh Sojoudi and Richard M. Murray. American Control Conference, 2010.
- A bio-plausible design for visual attitude stabilization, Andrea Censi, Shuo Han, Sawyer B Fuller, Richard M Murray. Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), 2009.
- A Real-Time Helicopter Testbed for Insect-Inspired Visual Flight Control, Shuo Han, Andrew D Straw, Michael H Dickinson, Richard M Murray. International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2009.