Programmable Molecular Technology Initiative: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== Objectives == | == Objectives == | ||
[[Image:pmti11.png|right|320px]] | |||
Biological organisms depend on remarkable molecular machines whose function is encoded within the molecules themselves – nucleic acid and protein sequences programmed by evolution to catalyze reactions, synthesize molecules, haul cargo, regulate development, and defeat pathogens. The proposed Programmable Molecular Technology Initiative (PMTI) will extend and exploit principles for engineering these versatile biomolecules with the mission of pioneering high-impact technologies centered in three focus areas: molecular instruments for readout and regulation of cell state, programmable molecular logic for selectively treating diseased cells while leaving normal cells untouched, and efficient microbial synthesis of biofuels from non-food renewable resources. | Biological organisms depend on remarkable molecular machines whose function is encoded within the molecules themselves – nucleic acid and protein sequences programmed by evolution to catalyze reactions, synthesize molecules, haul cargo, regulate development, and defeat pathogens. The proposed Programmable Molecular Technology Initiative (PMTI) will extend and exploit principles for engineering these versatile biomolecules with the mission of pioneering high-impact technologies centered in three focus areas: molecular instruments for readout and regulation of cell state, programmable molecular logic for selectively treating diseased cells while leaving normal cells untouched, and efficient microbial synthesis of biofuels from non-food renewable resources. | ||
Revision as of 17:44, 28 September 2013
The information on this page focuses primarily on the work involving my research group.
|
Current participants:
|
Collaborators:
Previous participants:
|
* Partially supported
Objectives
Biological organisms depend on remarkable molecular machines whose function is encoded within the molecules themselves – nucleic acid and protein sequences programmed by evolution to catalyze reactions, synthesize molecules, haul cargo, regulate development, and defeat pathogens. The proposed Programmable Molecular Technology Initiative (PMTI) will extend and exploit principles for engineering these versatile biomolecules with the mission of pioneering high-impact technologies centered in three focus areas: molecular instruments for readout and regulation of cell state, programmable molecular logic for selectively treating diseased cells while leaving normal cells untouched, and efficient microbial synthesis of biofuels from non-food renewable resources.
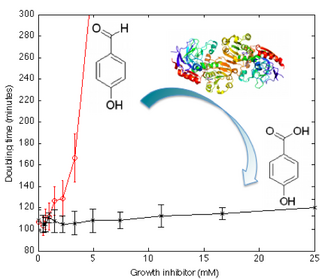
- Efficient microbial synthesis of biofuels from non-food renewable resources: We seek to achieve dramatic reductions in the cost of producing biofuels using re-programmed metabolic pathways in microbes, supporting an industrial revolution in the production of liquid fuels from renewable non-food resources. The focus of our work is in the re-programmed yeast stress response pathway that tolerates toxins generated during biofuel synthesis.
- Principles and foundations for programming molecular function: We seek to establish the underpinnings for future generations of programmable molecular technologies, including (1) languages, simulators and compilers for automated analysis and design of nucleic acid systems, (2) programmable self-organization of active molecular structures and (3) feedback control mechanisms for programming developmental patterning.
References
- Biomolecular resource utilization in elementary cell-free gene circuits, D. Siegal-Gaskins, V. Noireaux, and R. M. Murray. American Control Conference (ACC), 2013.